In a Class of its Own!
Our lead candidate, CB-24, is a first-in-class cancer therapeutic, which has shown remarkable results in pre-clinical and early clinical studies. While the drug has shown to be well tolerated by patients, it has been proven in early studies to be highly toxic to various cancer cells, and has induced disease stabilisation, partial remission, and even complete remission in some patients.
The following video briefly explains why we are so excited about CB-24:
— Overview —
Cancer is a global challenge that affects millions of people every year. The cost of treatment is rising, and the outcomes are often poor, especially for advanced stages of the disease.
Celtic Biotech is focused on some of the most common and deadly types of cancer, such as lung, breast, prostate, ovarian, and cervical cancer. These cancers account for a substantial proportion of cancer deaths worldwide, and there is an urgent need for better therapies.
We aim to provide safe, effective, and affordable solutions for cancer patients, with minimal side effects and reduced need for painkillers. Our products can be used alone or in combination with other treatments, depending on the patient’s needs and preferences.
Our candidates are capable of :
Killing cancer cells selectively, without harming healthy cells
Inhibiting the spread and growth of the cancer to other parts of the body
Overcoming drug resistance and relapse, which are common in conventional treatments
Enhancing the immune system’s ability to fight cancer
Improving the quality of life and survival rate of patients.
At Celtic Biotech, we are committed to improving the lives and well-being of cancer patients around the world. We believe that our products have the potential to revolutionise the field of cancer treatment and offer new hope for the future.
— Mechanism of Action —
CB-24 has a unique mechanism of action that differs from conventional chemotherapy or targeted therapy. It does not interfere with the DNA or metabolism of cells, but rather interacts with the cellular membrane of cancer cells. This makes it less toxic and more effective than existing treatments. Moreover, CB-24, and other neurotoxin based products in our suite, have a novel pattern of anti-cancer activity that is unlike any currently approved agents, making them a completely new category of molecular targeting therapies.
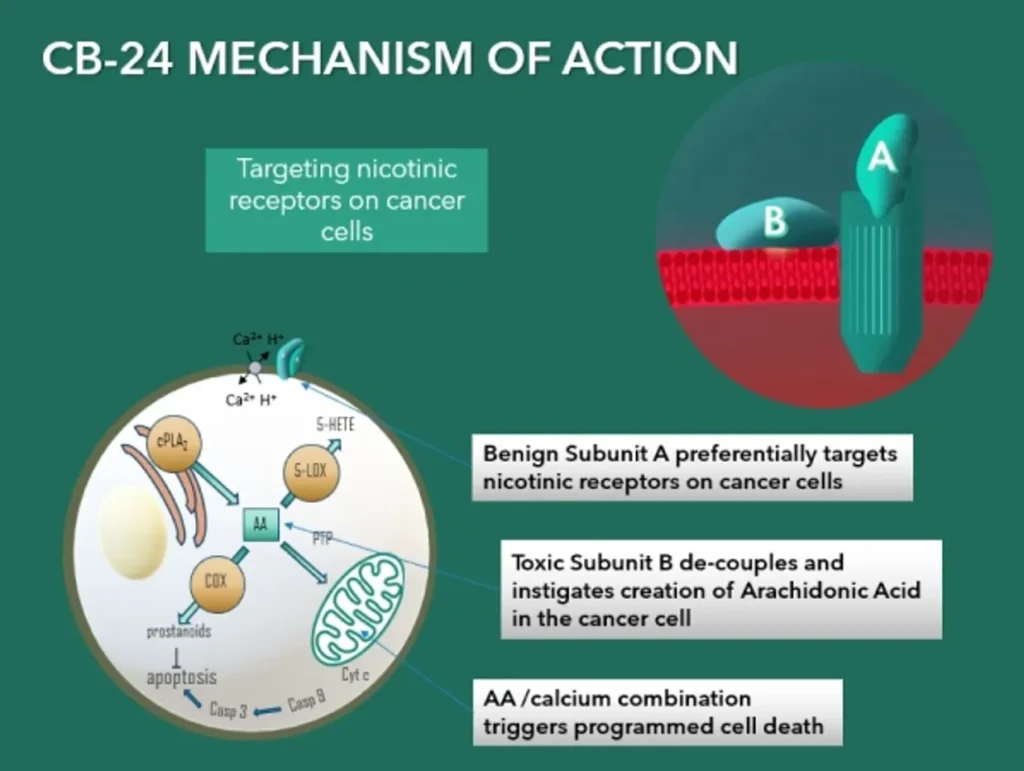
CB-24 is a nicotinic antagonist that can attach to several subtypes of nicotinic receptors. It is reported that alpha nicotinic receptors are highly expressed on a variety of malignant cell types (Pucci et al., Frontiers in Cellular Science. 2022), being enhanced due to remodelling of cellular membranes in malignant cells to include more negatively charged phospholipids such as phosphatidylserine (Szlasa et al., Bioenerg Biomembr. 2020). It has been well established that nicotine and nicotine-derived nitrosamines have been identified as the major and potent carcinogens. Upon binding of CB-24 to its receptor the PLA2 B subunit is released and attracted by the more negative membrane surface on the malignant cells, initiates its enzymatic action to digest the membrane releasing palmitate and arachidonic acid (Kattah et al., Toxicon 2002). The membrane is compromised and there is an influx of Ca2+ further activating L-type Ca2+ channels. Malignant cells have a significantly poorer membrane repair capacity compared to normal cells increasing their sensitivity to this form of attack (Frandsen et al., J Membrane Biol, 2016). Elevation of Ca2+ activates intracellular PLAs that further generate arachidonic acid triggering an intracellular cascade resulting in the synthesis of anti-apoptotic prostaglandins and lipoxygenase metabolism (Snider et al., PNAS, 1984) to produce LXA4 and its analogue 15-epi-LXA4 (Brigatte et al., Mediators Inflamm, 2016). Arachidonic acid causes apoptosis exclusively through the mitochondrial pathway which is preceded by permeability transitioning pore opening, cytochrome c release, and cleavage of caspase 9 and 3 LXA4 and its analogue 15-epi-LXA4 are potent immunomodulators that can also suppress tumour proliferation and modulate immune cells through formyl peptide receptors: a secondary and useful effect of CB-24.
